|

|
Refresh your browser to incorporate updates. Last updated March 14,
2009
History of Gluten Grain Intolerance
and other
important historical events
and trends in health.
The purpose of this page is not only to highlight the
gluten story, but also other lesser known historical medical events,
trends and research that may play into the gluten syndrome and/or health
in general. As societal and particularly children's health becomes a
puzzlingly disturbing issue in educated, technologically focused nations,
some of these previously abandoned or ignored ideas have been dusted off
and reexamined.
Interwoven are factors that some researchers believe may
underlie or contribute to the gluten syndrome:
Cellular vs Germ theory
- Germ theory favored drugs and processed food over health and wholeness.
Processed Food -
Wheat and milk resemble each other molecularly and are significantly
processed.
Toxins -
Toxins are fingered as the "big guns" in the gluten syndrome.
Fat trends -
Fats handle toxins, affect gut cell membrane, help digest grains, and
carry fat soluble vitamins.
Sugar/Carb/Yeast debate
- Sugars and yeasts contribute to gut dysfunction and immune cross
reactions.
 Here is a bookmarked table of contents for easy reference.
In order for the bookmarks to work, the links in which
Here is a bookmarked table of contents for easy reference.
In order for the bookmarks to work, the links in which
they belong must be clicked
open.
 Ancient History -
Early descriptions of digestive
complaints
Ancient History -
Early descriptions of digestive
complaints
 1700's BC - Digestive and related medical problems are mentioned in very ancient
documents such as the book of Exodus 23:25, 26 (BC 1700) 1700's BC - Digestive and related medical problems are mentioned in very ancient
documents such as the book of Exodus 23:25, 26 (BC 1700)
And
"And ye shall serve the LORD
your God, and he shall bless thy bread, and thy water; and I will take
sickness away from the midst (ie middle or can be 'bowels') of thee. There
shall nothing cast their young, nor be barren, in thy land: the number of
thy days I will fulfill."
100's
- 250? AD approximately - Aretaeus the Cappadocian
-
Secular medical literature alludes to descriptions that specifically resemble gluten or
possibly other food intolerances in writings from 100 AD, when a Greek
physician, Archaeus the Cappadocian described "The Coeliac Affection".
Francis Adams translated his description from Greek to English in
1856 for the Syndenham Society of England and translated the Greek term "koiliakos"
to the more accurate European term "coeliac". "Celiac" is the less
specific American version. They simply mean "belly or
abdominal".
(Medical
Meanings by William S. Haubrich p. 43)
Below is an Aretaeus quote from
Digital Hippocrates : The Extant works of Aretaeus
the Cappadocian. (picture at left)
ON THE CŒLIAC AFFECTION.
THE stomach being the
digestive organ, labours in digestion, when diarrhœa seizes the patient.
Diarrhœa consists in the discharge of undigested food in a fluid state;
and if this does not proceed from a slight cause of only one or two days'
duration; and if, in addition, the patient's general system be debilitated
by atrophy of the body, the Cœliac disease of a chronic nature is formed,
from atony of the heat which digests, and refrigeration of the stomach,
when the food, indeed, is dissolved in the heat, but the heat does not
digest it, nor convert it into its proper chyme, but leaves its work half
finished, from inability to complete it; the food then being deprived of
this operation, is changed to a state which is bad in colour, smell, and
consistence. For its colour is white and without bile; it has an offensive
smell, and is flatulent; it is liquid, and wants consistence from not
being completely elaborated, and from no part of the digestive process
having been properly done except the commencement.
Wherefore they have flatulence of the stomach, continued eructations, of a
bad smell; but if these pass downwards, the bowels rumble, evacuations are
flatulent, thick, fluid, or clayey, along with the phantasy, as if a fluid
were passing through them; heavy pain of the stomach now and then, as if
from a puncture; the patient emaciated and atrophied, pale, feeble,
incapable of performing any of his accustomed works. But if he attempt to
walk, the limbs fail; the veins in the temples are prominent, for owing to
wasting, the temples are hollow; but also over all the body the veins are
enlarged, for not only does the disease not digest properly, but it does
not even distribute that portion in which the digestion had commenced for
the support of the body; it appears to me, therefore, to be an affection,
not only of the digestion, but also of the distribution.
But if the disease be on the increase, it carries back the matters from
the general system to the belly, when there is wasting of the
constitution; the patients are parched in the mouth, surface dry and
devoid of sweat, stomach sometimes as if burnt up with a coal, and
sometimes as if congealed with ice. Sometimes also, along with the last
scybala, there flows bright, pure, unmixed blood, so as to make it appear
that the mouth of a vein has been opened; for the acrid discharge corrodes
the veins. It is a very protracted and intractable illness; for, even when
it would seem to have ceased, it relapses again without any obvious cause,
and comes back upon even a slight mistake. Now, therefore, it returns
periodically.
This illness is familiar to old persons, and to women rather than to men.
Children are subject to continued diarrhœa, from an ephemeral intemperance
of food; but in their case the disease is not seated in the cavity of the
stomach. Summer engenders the disease more than any other of the seasons;
autumn next; and the coldest season, winter, also, if the heat be almost
extinguished. This affection, dysentery and lientery, sometimes are
engendered by a chronic disease. But, likewise, a copious draught of cold
water has sometimes given rise to this disease.
300 AD - A Roman physician
- described a diarrheal condition similar to celiac disease, for which he
suggested plantain juice and fasting.
Management of Celiac Disease
- SV and MP Haas, JB Lippincott Co., Philadelphia (from Breaking the
Vicious Cycle, Elaine Gottschall)
1745 - Prince
Charles Young Pretender to the Enlish throne is reported to have suffered
ulcerative colitis and recovered on a milk free diet.
Cereals and Schizophrenia -
data and hypothesis. Acta Psychiatry Scandinavia 42:125-152. (from
Breaking the Vicious Cycle, Elaine Gottschall)
 Close:
Ancient History
Close:
Ancient History
 The 1800's
-
Cellular vs. Germ theory debate and Samuel Gee The 1800's
-
Cellular vs. Germ theory debate and Samuel Gee
The following paragraph is a quote
thanks to Dr Stefano Guandalini, MC, U of Chicago Celiac Disease Center
IMPACT newsletter, summer 2007, Vol 7 Issue 3. Click for his
detailed full article
Matthew Baillie -
In the early 19th
century, a Dr. Mathew Baillie probably unaware of Aretaeus, published his
observations of a "diarrheal disease of adults causing malnutrition and
characterized by gas - distended abdomen. He even went on to suggest
dietetic treatment, writing, "Some patients have appeared to derive
considerable advantage form living almost entirely upon rice. His
observations, however, went practically unnoticed.
Underlying
concepts that fundamentally influence research today.
Germ theory vs Cellular theory - By the mid 1800's the invention of stronger
microscopes afforded researchers a new view of microbiology. Two well known
French scientists, Louis
Pasteur and Antoine Bechamp both saw the same images under their microscopes but interpreted what they saw
differently. Their opposing ideas were a subject of debate in the
French Medical Society for the
rest of the century. They both passed away around the turn of the 20th century. The opposing camps of opinion held a "showdown" in
which each presented proofs. It is believed by some cellular
theorists today that the
cellular (or soil) theory
proofs were bungled and mainstream science adopted Pasteur's
germ theory as
the basis interpretation of research until the present. However, predictions of
the cellular theorists have come true and some research today
appears to support some of these ideas.
 Louis Pasteur
1822 - 1895, France - A well known historical figure and French
government scientist, Louis Pasteur believed the strange shapes he saw
under his microscope were various "germs". A specific germ always
appeared with a specific disease. He postulated that they were
responsible for that specific disease, and should be eliminated.
When they were "killed" the disease disappeared. Between 1850
and 1900 he developed immunizations or “biologicals” to combat these
"germs", and introduced pasteurization of poor quality, infected milk in
order to heat kill "germs" in the milk. A search for drugs
and methods to
destroy these "germs" has become the focus of research to this day. Louis Pasteur
1822 - 1895, France - A well known historical figure and French
government scientist, Louis Pasteur believed the strange shapes he saw
under his microscope were various "germs". A specific germ always
appeared with a specific disease. He postulated that they were
responsible for that specific disease, and should be eliminated.
When they were "killed" the disease disappeared. Between 1850
and 1900 he developed immunizations or “biologicals” to combat these
"germs", and introduced pasteurization of poor quality, infected milk in
order to heat kill "germs" in the milk. A search for drugs
and methods to
destroy these "germs" has become the focus of research to this day.
 Antoine Bechamp
1816 - 1908, France - Independent researchers including respected and capable Antonie Bechamp, a
peer of Pasteur, disagreed with Pasteur’s interpretations. Bechamp and
others they believed
the "microbes" morphed depending on their
environment and the "job" they needed to perform. They believed
deterioration and disease was created by poor conditions, such as toxins, inadequate
nutrition, rest, fresh air, etc. The microbes morphed and appeared
when needed in the form required to act as "janitors" or to perform other
duties. They were blamed for the disease because
they were always found on the scene. This is similar to blaming the fireman,
policeman or garbage collector for
the fire because he is there to deal with some aspect of the fire. These
microbes produced excretions of their own that often caused symptoms such
as vomiting, diarrhea, etc., which caused waste products and toxins to
ultimately be removed from the body. Therefore, "killing" the
microbes does often stop symptoms. However this leaves the original
cleanup work unfinished and
if the underlying deficiency or toxin is allowed to advance, further
deterioration may prompt microbes to return
in worse forms later, to "scavage" a worse mess. Bechamp
and others predicted that "germ theories" would send research on a wrong
turn. Bechamp's final treatise "The
Third Element of the Blood" explains
and defends his position. Antoine Bechamp
1816 - 1908, France - Independent researchers including respected and capable Antonie Bechamp, a
peer of Pasteur, disagreed with Pasteur’s interpretations. Bechamp and
others they believed
the "microbes" morphed depending on their
environment and the "job" they needed to perform. They believed
deterioration and disease was created by poor conditions, such as toxins, inadequate
nutrition, rest, fresh air, etc. The microbes morphed and appeared
when needed in the form required to act as "janitors" or to perform other
duties. They were blamed for the disease because
they were always found on the scene. This is similar to blaming the fireman,
policeman or garbage collector for
the fire because he is there to deal with some aspect of the fire. These
microbes produced excretions of their own that often caused symptoms such
as vomiting, diarrhea, etc., which caused waste products and toxins to
ultimately be removed from the body. Therefore, "killing" the
microbes does often stop symptoms. However this leaves the original
cleanup work unfinished and
if the underlying deficiency or toxin is allowed to advance, further
deterioration may prompt microbes to return
in worse forms later, to "scavage" a worse mess. Bechamp
and others predicted that "germ theories" would send research on a wrong
turn. Bechamp's final treatise "The
Third Element of the Blood" explains
and defends his position.

The following paragraph is a quote
thanks to Dr Stefano Guandalini, MC, U of Chicago Celiac Disease Center
IMPACT newsletter, summer 2007, Vol 7 Issue 3. Click for his
detailed full article
Samuel Gee, 1839 - 1911, London, England -
and it was for the English
doctor Samuel Gee, a leading authority in pediatric diseases, to take full
credit for the modern description of celiac disease some 75 years later,
when he gave a lecture to medical students on the "celiac affection," the
milestone description of this disorder in modern times.
Like Baillie, Gee sensed that
"if the patient can be cured at all, it must be by means of diet." He
added that "the allowance of farinaceous food must be small", and also
described "a child who was fed upon a quart of the best Dutch mussels
daily, throve wonderfully, but relapsed when the season for mussels was
over; next season he could not be prevailed upon to take them." Thus he
documents the improvement following the introduction of a gluten-free
diet, and the relapse after reintroduction of gluten. His famous quote,
"We must never forget that
what the patient takes beyond his ability to digest does harm."
Samuel Gee's description of coeliac disease is as follows.
"There is a kind of
chronic indigestion which is met with in persons of all ages, yet is
especially apt to affect children between one a five years old. Signs of
the disease are yielded by the fæces; being loose, not formed, but not
watery; more bulky than the food taken would seem to account for; pale in
colour, as if devoid of bile; yeasty, frothy, an appearance probably due
to fermentation; stinking, stench often very great, the food having
undergone putrefaction rather than concoction."
Quote Dr Guandalini
As the decades passed, there
was still no clue as to what could be causing celiac disease and no hint
(in spite of autopsies frequently performed given the high mortality rate)
of the damage to the intestinal mucosa. Yet some
of the present-day
findings, which we tend to consider as recent advances, were indeed well
known long ago, including that celiac disease could be present without
diarrhea, the protective role of breast-feeding in the development and
severity of celiac disease, only recently documented, and the increased
incidence in families, particularly twins.
 Close:
The 1800s
Close:
The 1800s
 1900's
- 1950's
Degeneration Studies, Carbs vs Protein (Gluten) Debate 1900's
- 1950's
Degeneration Studies, Carbs vs Protein (Gluten) Debate
Processed foods
appear followed by widespread degeneration of societal health
Professionals who practiced
between 1900 and 1930 observed such a sharp decline in public health and a
rise in digestive disorders, heart conditions and many others that some of
them set out to find answers. They and also many missionaries and
explorers were impressed by the contrast in health between peoples who
still subsisted on centuries old dietary practices dictated by their local
environments, and the deteriorating health of western civilizations.
Modern societies had switched to “displacing foods of modern commerce”,
mainly processed white flours and sugars, canned milk, meats and vegetables, and new hydrogenated vegetable oils such as the 1911
introduction of
“Crisco.”
This research not specifically
gluten focused - but on the general
effects of processed food in societies around the world.
Dr. Weston A Price DDS (1870-1948)
- One careful
researcher, a respected Cleveland dentist,
Dr. Weston A. Price, traveled to many
isolated cultures in the 1930's to observe these peoples, their diets, food preparation methods, and their overall health.
He lined up villages to count cavities, made notes on general health, and
took food and saliva samples back to his laboratory. He
found 11 consistent dietary and cultural similarities between these
very diverse isolated peoples around the world. He also
found overall better health in the traditional cultures, and fine, straight teeth set in wide faces,
with dental arches that had plenty of room for wisdom teeth, and very low
incidences of cavities. He also observed a heartbreaking decline in
overall health, susceptibility to illness, and “dental deformities”,
meaning narrowed dental arches and crowded crooked teeth, other physical degradations, and many
degenerative health conditions wherever these peoples came in contact with
civilization and adopted modern foods. Other researchers of his era who performed
similar studies had parallel findings.
Brochure in the 1930's to observe these peoples, their diets, food preparation methods, and their overall health.
He lined up villages to count cavities, made notes on general health, and
took food and saliva samples back to his laboratory. He
found 11 consistent dietary and cultural similarities between these
very diverse isolated peoples around the world. He also
found overall better health in the traditional cultures, and fine, straight teeth set in wide faces,
with dental arches that had plenty of room for wisdom teeth, and very low
incidences of cavities. He also observed a heartbreaking decline in
overall health, susceptibility to illness, and “dental deformities”,
meaning narrowed dental arches and crowded crooked teeth, other physical degradations, and many
degenerative health conditions wherever these peoples came in contact with
civilization and adopted modern foods. Other researchers of his era who performed
similar studies had parallel findings.
Brochure
 Dr.
Francis Pottenger MD
(1901 - 1967)
studied over 900 cats in
the 1930's in Los Angeles, CA. His interest was to discover the
effects of heat processed foods vs. raw food on cats. Dr. Pottenger
found that the health of the cats degenerated significantly with each
generation they consumed processed food, particularly since cooking
destroys taurine, an amino acid needed by cats (and humans but to lesser
degree)
Dr. Price and
Dr. Pottenger's
final research conclusions were that "adoption
of the "displacing foods of modern commerce," was disastrous for all
groups studied" Simply
put, "Processed food is NOT OK"
Research
today on the effects of processed wheat supports this conclusion.
Note: This file contains 2 articles. Scroll to the top for the
Vojdani article. Dr.
Francis Pottenger MD
(1901 - 1967)
studied over 900 cats in
the 1930's in Los Angeles, CA. His interest was to discover the
effects of heat processed foods vs. raw food on cats. Dr. Pottenger
found that the health of the cats degenerated significantly with each
generation they consumed processed food, particularly since cooking
destroys taurine, an amino acid needed by cats (and humans but to lesser
degree)
Dr. Price and
Dr. Pottenger's
final research conclusions were that "adoption
of the "displacing foods of modern commerce," was disastrous for all
groups studied" Simply
put, "Processed food is NOT OK"
Research
today on the effects of processed wheat supports this conclusion.
Note: This file contains 2 articles. Scroll to the top for the
Vojdani article.
The carbohydrates vs
gluten debate
(sugar/starch vs protein)
As digestive disorders and
many other health conditions increased, much excellent
research was
performed between 1900 and 1950. In the 1950's a debate among professionals arose
over the role of carbs vs. protein (gluten) that exists to this day. Perhaps all sides are
correct to some degree depending on the case. (Later, by the 1980's,
"most carbohydrates and sugars" were fingered in overgrowth and treatment of candida/yeast issues.)
Some researchers:
1. focused on permanent
removal of certain grain proteins -
Gluten Free Diet.
2. focused on temporary
removal of specific carbohydrates (sugar, starch) -
Specific Carbohydrate
Diet
3. focused on temporary
removal of all sugars and starches -
Candida/Yeast Diets More
candida diets
Carbohydrate research came
first.
Reference, Breaking the Vicious Cycle, Elaine Gottschall
Between 1900 and 1950 several researchers and their assistants handed off
their work from one to to the other as they passed on. They all
focused on starches and sugars.
1908 - Drs.
Emmett Holt Sr, Bellevue Hospital and Christian Herter, Columbia
University published "On
Infantilism from Chronic Intestinal Infection".
Remarkably they proposed that the nervous system was a main target of the
disease and that
"the most frequent cause of
relapses is the attempt to encourage growth by the use of increased
amounts of carbohydrates."
1921 - Drs. John
Howland and Sydney V. Haas. Dr. Howland and Haas were Dr. Holt's
younger assistants at the Vanderbilt clinic and were inspired to carry on
his work. Dr. Howland presented his paper "Prolonged Intolerance to Carbohydrates"
in 1921 to the American Pediatric Society. Again, he focused on
removal of carbohydrates.
Dr.
Sidney Valentine Haas
1870 -1964
Dr. Haas agreed with his colleague Dr. Howland, but he
searched for carbohydrates that agreed with his patients to increase their
nutrition. He discovered bananas and banana flour worked well and he
continued to develop a diet which included fruits and vegetables
containing monosaccarides only (very simple sugar molecules that
required no digestion).

Sidney Haas and his
professional forebears all focused on problematic undigested starches and
sugars in grains, starchy vegetables, refined sugars and other complex carbohydrates
with claims of 600 cures.
http://www.scdiet.org/7archives/scdceli1.html
One year after Sidney
Haas published his research on
carb digestion, attention turned away
from carbohydrates to
focus on only the gluten (protein) in only certain grains. Soon after
this debate arose, however, Herb and Elaine Gottschall appeared on the scene,
Dr. Haas passed, and Elaine Gottschall continued
Dr. Haas' work.
Herb and
Elaine Gottschall,
parents of 8 year old Judy, found Dr. Haas, age 92 in New York. Judy was scheduled for
colon removal but his recommendations saved need for surgery and probably
spared Judy's life. Herb sent Elaine
back to school to discover why Dr. Haas' diet succeeded when all the
other doctors failed. Elaine attended university 19 years, became a
biochemist, and continued Dr. Haas' work. She formulated the Specific Carbohydrate Diet, (SCD), in
it's present form, which
removes not only all gluten grains, but all grains, and other foods which
contain certain complex sugars. This or similar diets beyond the gluten free
diet are increasingly used
today by patients with ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease,
autistic children and other digestive and psyschiatric disorders.
She claims, as did Dr. Haas, that this diet can in some cases completely
cure patients to a degree that they can reintroduce healthy forms of
grains and starches. Elaine made it clear that this diet helps
many but not all patients.
Attention turns from
carbs to protein (gluten) - World War 2 - 1950's
Dr. Willem Dicke,
1905 - 1962, Holland
a
Dutch pediatrician, had previously noted that some sick children in
his practice improved during World War 2 when gluten grains were
unavailable, and deteriorated when these grains were again available.
were again available.
Here is another quote from
Dr. Guandalini - "Dicke
had noticed that during bread shortages in the Netherlands caused by World
War II, children with celiac disease improved. He also saw that when
Allied planes dropped bread into the Netherlands, they quickly
deteriorated. A few years later, working with others, he produced a series
of seminal papers, documenting for the first time the role that gluten
from wheat and rye plays
in celiac disease.
This quote thanks to the
ww.csaceliac.org website Dr.
Willem Karel Dicke, a Dutch pediatrician, recognized in 1952 that the
disease is caused by the ingestion of wheat proteins. He wrote his
doctoral thesis on the subject for the University of Utrecht in 1950. By
1954, Dicke, Charlotte Anderson and a number of their colleagues, working
in Birmingham, England confirmed the treatment and described the
histologic damage to the intestinal mucosa as being directly related to
celiac disease.
Here is another quote from
Dr. Guandalini-
The next major breakthrough
came in the mid-50s, when
Margot Shiner described a new jejunal biopsy
apparatus with which she successfully reached and biopsied the distal
duodenum. This – and the development of the less cumbersome capsule
developed shortly after by the American Lieutenant Colonel Crosby -- finally allowed
doctors to link the disease with a specific, recognizable pattern of damage to the
proximal small intestinal mucosa."
NOTE: The carb vs protein
(gluten) debate is important! It
is worth the time to read both sides and apply the information to one's
own situation. Perhaps carbs and/or gluten are both problems
depending on the case. Some patients begin with the Gluten Free Diet and
later go
further to the stricter Specific Carbohydrate Diet or a Candida/Yeast
Diet or other similar carbohydrate based diets. Here are papers from both sides to compare:
The carbohydrate perspective by Elaine Gottschall
The protein (gluten) perspective by Dr. Stephano
Guandalini
(By the 1970's another even
stricter diet appeared, the Candida/Yeast Diet and versions of it. )
The candida/yeast perspective - Dr. William Crook
and
Bee Wilder's Candida support program
Coming - More circa 1930's
research Much fascinating research was
performed between 1900 and 1950 which has been ignored or forgotten as
corporate and industrial interests powered the direction of science,
medicine and politics. This list does not include a number of these
scientists passed over by mainstream medical history. They may have
important contributions to a better understanding of our current health
crisis. As time permits, short biographies of these researchers will
be added to this page.
Later 1950's - Gluten
focused, villi damage celiac is assumed "rare", and
nearly forgotten
The gluten centered
perspective led to a 1950's diagnostic criteria
for "celiac" disease, based on an autoimmune reaction limited to gluten based grains.
Symptoms included diarrhea, short stature,
failure to thrive, frothy pale stools, and general digestive troubles.
At first diagnosis was symptom based, but soon endoscopes and blood
tests appeared and diagnosis was further limited to only positive
antibodies,villi damage and villi regrowth on the gluten free
diet. Sometimes a gluten challenge was required document regression and
villi regrowth a second time for final diagnosis.
Unfortunately, only a few of
the many patients ill with digestive complaints fit the exceedingly narrow
celiac criteria. Attention
turned away from carbohydrates AND gluten for several decades. Paradoxically,
digestive illness continued to rise, but "Celiac disease" was
thought to be extremely rare in the United States. Medical students received minimal
training (20 minutes), and were told they would probably never see a case
in their practice. Therefore US doctors knew of celiac disease but rarely considered or tested for it. Patients waited an
average of 11 years for diagnosis if they were ever diagnosed at all. Many
of these unfortunate sufferers were labeled with a catch all term,
"Irritable Bowel Syndrome", and advised to manage their
particular
symptoms with antidiarrheals, antacids and constipation aids. Non
digestive ailments such as headaches, seizures, autoimmunity, inflammation
or nutritional deficiencies were rarely connected at all. It was nearly
the year 2000 before this situation changed in the US.
 Close:
1900s
- 1950s
Close:
1900s
- 1950s
 1960's
- 2000
Industrialized fast food vs. Back to the Earth
movement 1960's
- 2000
Industrialized fast food vs. Back to the Earth
movement
Chemical and toxin use in
agriculture and processed food - After World War 2 and subsequent wars,
left over chemical warfare products were put to use as agricultural
insecticides. Chemicals and thousands of artificial substances in agriculture, the food
supply and environment increased dramatically over the years. NOW they
are fingered as
relevant by segments of the gluten syndrome and autism communities and other health
groups. Many researchers insist
that while genes predispose and may explain the occasional case of
gluten reactivity in previous centuries, perhaps still in combination with
toxic exposures, TOXINS themselves are the "big guns"
today. Toxins are now thought by many researchers to degrade the
gut wall and expose a much higher percentage of the general population to
an immune response to gluten.
1960's -
Hippies demanded organics and unprocessed
grains such as whole wheat during the "Back to the Earth" movement.
Although
the
hippies realized food processing robbed them of nutrition they did not
consider that
their
whole wheat had been harvested dry with modern equipment. It
was not
exposed to the elements as in the old days when shocks stayed out in
weather and were built with a "cap" to "sweat" the grains. Thus
the
exposure to moisture and subsequent drying in the sun neutralized phytotoxins
in the bran, and released enzymes inside the kernel that assist the body in
digestion of the grain. The whole grain movement of the 1960's
milled unsoaked
grain with phytotoxins still in the bran, and then due to the
1970's lowfat trend, reduced the fats eaten with it
that aid grain digestion. Furthermore
hydrogenated margarine was often substituted for natural traditional butter. See
Wheaty
Indiscretions WAPF
1970's - Low Fat-No fat-Vegetable
oils - Natural saturated animal and tropical fats were demonized,
(butter animal fat, coconut oil and palm oil) and replaced with processed liquid and hydrogenated
vegetable oils containing transfats. These were claimed more "heart
healthy" even though huge research projects such as the Framing ham
Heart Study showed otherwise. Some patients today trace their digestive problems back to when
they jumped on the whole wheat, low fat bandwagon in the early '70's.
Interestingly, after the low fat trend became established, the fat soluble
Vitamin E awareness fad began. See
The Oiling of America
1970's - European doctors caught on to protein/gluten based celiac disease in the
1970’s and diagnosis rates climbed accordingly. While an American patient
waited on the average for 11 years for a celiac diagnosis, if they were
fortunate enough to be diagnosed at all, eventually a
European patient was identified in only a few weeks.
1980's - Interest in sugar,
carbohydrates and yeast/candida related illnesses reappeared in the US
with "Sugar
Blues" 1975, by William Dufty, and "The
Yeast Connection", 1986, by William G. Crook.
1990's - The Four Food Groups
were
replaced by the
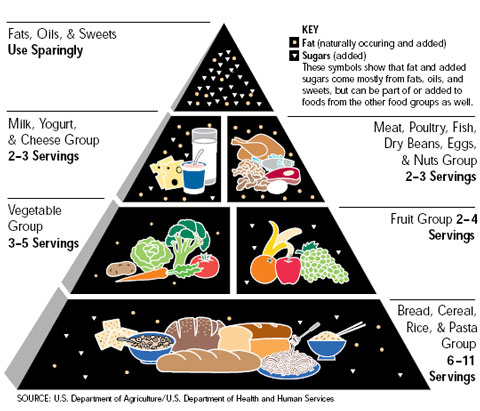 Food
Pyramid with grains on the bo Food
Pyramid with grains on the bo
replaced in 1992
by the Food Pyramid with
o grains on the
bottom and fats at the top.

History of US Dietary Recommendations
1990's - Early 1990's An
expanded vaccination schedule
for infants and children was put in place and enlarged upon in the ensuing
years . A
debate arose thereafter over Thimerosal
(a mercury based disinfectant) and other additives as well as the
safety of some of the vaccinations
themselves, as the rates of
autism in children rose dramatically.
1990's -
Cell phone coverage and other forms of
electrosmog such as wireless internet,
cordless phones, microwaves, and other
exposures grew steadily throughout the 1990's and until present until most
of the United States is now exposed to
cell phone radiation. Research on
the health benefits/dangers of
cell phone and electrosmog exposure brings deeply troubling
issues to light including concerns that the
gut and blood
brain barriers may be altered by such radiation. This is
of direct concern to the gluten syndrome and allergy/intolerant
communities as
disturbed tight junctions between gut and
other barrier cells is a major instigator of gluten reactivities.
 1992's
- The
US was challenged in the early 1990's and forced to hear the "celiac story" in 2003 -
Dr. Alesio Fasano, a young gastroenterologist from Naples, Italy, joined the University of Maryland research team
in the early 1990’s. He ran a routine search in the University of Maryland hospital computer for the
number of celiacs diagnosed in the past 10 years. To his astonishment, the
search returned one case. His reaction, “Where are the American
Celiacs?” He refused to be deterred by colleagues who insisted "It's
not here in America." Alesio's courageous insistence that many
Americans do have "celiac disease", backed by prompt diagnosis of patients
under his care led to a 5 year study to establish prevalence rates in
the US. The project included approximately 15,000 patients across 32
states. At the end of the study, Dr. Fasano was right. New figures
showed that 1 in 133 Americans sampled from the healthy population, and 1
in 56 in the symptomatic population had villi damaged celiac disease. They were 97%
undiagnosed! The study was published in the Archives of Internal Medicine,
Feb, 2003. Subsequent studies support 1 : 100 in the healthy
population. Dr. Alesio
Fasano, left, Rich Gannon, right 1992's
- The
US was challenged in the early 1990's and forced to hear the "celiac story" in 2003 -
Dr. Alesio Fasano, a young gastroenterologist from Naples, Italy, joined the University of Maryland research team
in the early 1990’s. He ran a routine search in the University of Maryland hospital computer for the
number of celiacs diagnosed in the past 10 years. To his astonishment, the
search returned one case. His reaction, “Where are the American
Celiacs?” He refused to be deterred by colleagues who insisted "It's
not here in America." Alesio's courageous insistence that many
Americans do have "celiac disease", backed by prompt diagnosis of patients
under his care led to a 5 year study to establish prevalence rates in
the US. The project included approximately 15,000 patients across 32
states. At the end of the study, Dr. Fasano was right. New figures
showed that 1 in 133 Americans sampled from the healthy population, and 1
in 56 in the symptomatic population had villi damaged celiac disease. They were 97%
undiagnosed! The study was published in the Archives of Internal Medicine,
Feb, 2003. Subsequent studies support 1 : 100 in the healthy
population. Dr. Alesio
Fasano, left, Rich Gannon, right
1996 - New organisms in the food
supply - Genetically modified crops
were first grown in the United
States in 1996. These new foods entered the world market unlabeled.
They attracted attention more quickly in the UK and
Europe, and were labeled "Frankenfoods" in a storm of protest, but it was
nearly 7 years before the US began to notice their presence.
1996 -
Mario Hadjivassiliou - published an article of gluten and neurology
Does cryptic gluten sensitivity play a part in neurological illness? Feb
1996
 Close: 1960s - 2000
Close: 1960s - 2000
 2000 -
Degeneration,
toxins, GMO's, gluten awareness vs organic trends
2000 -
Degeneration,
toxins, GMO's, gluten awareness vs organic trends
By the turn of the century,
autoimmunity, degenerative disease, obesity, autism, ADD, diabetes,
cancer digestive and mental illnesses were obviously on the rise.
Children's health was an increasing concern. In response, the
movement back to sustainable organic agriculture and Weston Price style
traditional dietary habits began to gain ground rapidly. Local organic
sources became more easily available and trendy.
2000 - Dr. Ken
Fine opened
Enterolab in Dallas Texas to research
the gluten syndrome and make available to the public a home stool test by
mail order.
2003 -
Seeds of Deception was published,
a call to arms regarding
genetically modified crops. Jeffrey Smith, an employee at a genetics lab,
spawned a wave of awareness and unease regarding gmo's and diet in general.
2003 -
Prevalence of Celiac Disease in At- Risk and
Not-At-Risk Groups in the United States
was published in the
Archives of Internal
Medicine, Vol 163, February 10, 2003 286-292 Relief was finally on the way for many celiac sufferers in
the United States, but as is often the case the story was not as simple as
it first appeared. Confusion and disjointed dynamics often occurred
as the media, medical community and general public were made aware of this
disease simultaneously. Medical practitioners in many disciplines
were forced to scramble for new information as patients approached them
for tests and treatment.
Understandably many doctors brushed off their patient's requests to be
tested. Indeed many patients who were sure they would turn up
positive tests, in fact did not, even patients who already suspected
gluten was a problem. Laboratories that rarely ran celiac screens
were deluged with sensitive tests that their operators were not
experienced enough to run properly or interpret accurately. Much
frustrating effort was expended by celiac specialists to educate
their professional colleagues. Often they were initially ignored or worse,
deprecated, by their peers. Doctors who responded and learned quickly were
appreciatively dubbed by some support groups as "heads up doctors".
All of our celiac and gluten syndrome specialists have worked very hard
and taken a beating to bring this syndrome to our attention.
2004 - A drug for the gluten
syndrome? - Dr. Fasano and a team of scientists formed Alba
Therapeutics to develop a
genetically modified (recombinant) drug
which is
currently in testing
to begin to treat the gluten syndrome. The drug works by manipulating a
chemical they recently discovered and named "Zonulin". Zonulin controls the
opening and closing of "gateways" in the gut wall which allow certain
items to pass across the gut wall into the body. In the presence of
inflammation, high levels of zonulin change may cause these "gateways" to
malfunction and allow molecules such as undigested gluten to slip into
places they are not intended to be and then the immune system reacts.
The drug is currently being testing on real celiac patients, but it is not
ready for market at this time. It is not intended to replace the gluten
free diet but for occasional use in unusual situations. (Feb 2009)
Why so many negative testers who respond to the diet?
Meanwhile, to complicate matters, as word of the new research spread among
newly diagnosed celiac
patients, some family members had no symptoms at all but were tested anyway
since the disease often has a genetic component. In many cases they
tested positive (antibodies and damaged villi) with no hint of symptoms,
and were labeled "silent celiacs". In other cases symptomatic family members and friends realized they
also had many symptoms of celiac disease. However many of them tested
negatively for the antibodies or villi damage required for formal diagnosis. Some of them tried the diet and many discovered that indeed they improved. Others, confused by their negative tests,
gave up the gluten free diet even though they felt better, or never tried
the diet at all. Still others went gluten free sometimes with dramatic
improvement, but intentionally went back to gluten for
a period of weeks or months in order to be tested. They did this
to obtain
their “magic celiac diagnosis”, to socially confirm their need for this “funny diet”.
Unfortunately, those patients often found the “gluten challenge” very very
miserable and some have been damaged by it. Their bodies
seemed
much more sensitized to the effects of gluten the second time around. Unfortunately, many of these
non celiac gluten syndrome patients who had already discovered they
should avoid gluten, received negative test (antibody and biopsy), despite
misery during and even after their gluten challenge. Many were misled back
to their old problems on a gluten diet. Others listened to their
body's clear messages and went gluten free permanently anyway.
2005 - Non celiac gluten syndrome patients appear to comprise a
majority of the gluten reactive community. Unfortunately,
comparatively little
research has been performed on this puzzling group of patients. For decades ALL research on gluten intolerance
was performed on biopsy
diagnosed celiacs. Many doctors recognized that their negative testing
patients improved on a gluten free diet, but they
hesitated or refused to recommend a strict gluten free diet with no
research or diagnostic criteria to back up their diagnosis. This left most
a majority of gluten intolerant
patients in a medical “No Man’s Land”, forced to make their own decisions
as best they could determine. Often this undiagnosed state led to
poor compliance and further deterioration of health. A concern arose
that more patients were misled by the celiac story as understood at the
time than those who had villi damage and received a celiac diagnosis.
2005 - The continuing
carbohydrate story - Elaine Gottschall peacefully passed away
September 5, 2005, age 84. Elaine is the courageous mom who went
back to college at age 47 at her husband's urging after Dr. Sidney Haas'
specific carbohydrate diet healed their 8 year old daughter Judy.
Before her death she finally was afforded the recognition she well earned
for her help to many many persons suffering from a range of disorders
including autism, crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and many many
others.
The Specific Carbohydrate Diet is gluten
free but goes beyond and focuses instead on the types of sugars and
carbohydrates in the diet. The SCD Diet is used extensively in biomedical
autism circles. As with most other diets, it clearly helps many but
not all patients. Personal
tribute
Obituary
2006 - New labeling laws
aid patients with allergies and intolerances. - new labeling
laws went into effect January 2006. They required the 8 top US
allergens to be clearly labeled on all food items. This list
included wheat, soy, milk, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts and peanuts.
This litigation helped gluten intolerant patients partly but not
completely since barley, rye and oats were not included in the list.
Further amendments are still in progress and the definition of "gluten
free" was still undetermined. The general skeptical public was
forced to take gluten more seriously when they saw gluten and wheat
labeled on their food products.
Dec, 2006 - New York city
banned transfats in unpackaged food.
A major victory for
Mary Enig and peers, who worked to
document and raise
awareness of
transfat dangers since the 1960's. (The
Rise and Fall of Crisco)
"Interesterification"
quickly replaced transfats, unlabeled. Some researchers have expressed
concern that
interesterified fats do not contain
transfats, but do still contain an
artificially changed molecule that the body has never seen. These
fats are found in vegetable oils that are processed into a partially
hardened, soft spread state, ie no longer in their liquid state. Some
researchers recommend that
butter, virgin
coconut or
palm oil, or
naturally raised animal fat be used in
place of vegetable oils and soft tub fats or margarines. Articles that
explain interesterified
fats are sometimes
noncommittal as to their effects.
Transfats are not required to
be labeled if their weight per serving is under .5 gram.
Therefore it is easier to check ingredients by looking for
hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated vegetable oils.
Interesterified fats are still hydrogenated but do not contain transfats.
Almost all baked goods contain processed hardened or partially hardened
vegetable oils.
2008 -
Statistically about 30% of patients diagnosed with villi damage do not
improve on the gluten free diet alone, or they may improve at first and
then some of their issues return. They usually find they need to
severely reduce their intake of gluten free substitutes. They are
still mostly junk foods. Some folks remove all grains, or do the
Specific Carbohydrate Diet, a
Candida, or
Body Ecology type diet and often
they switch to organic, more raw foods, and a Weston Price based dietary
lifestyle. Processed and fast foods gradually are abandoned for
fresh farm products and more homemade meals. Toxic cleaners,
personal care items, and often plastics, microwaves and wireless devices
also are replaced with greener and healthier alternatives. Many
patients find that going gluten free is the start of a lifestyle
revamp, and once they go gluten free the other changes come easier.
Many also find nutritionally oriented professionals to help them treat
problems that the gluten damage triggered such as nutrient loss.
A celiac
vaccine?
Clinical trials were to start in 2008.
Update here. Website: www.nexpep.com.au
2009 - The non
celiac gluten syndrome hordes are out of the closet. "Self
diagnosis" is no longer perceived as wishful thinking by most of the gluten syndrome community.
Even the most staunch "celiac" specialists admit this huge group exists,
although they still mostly teach that non celiac gluten reactivity is not autoimmune.
Other researchers emphatically insist it IS often autoimmune, and
clinically many in the gluten syndrome community fit this concept. There is
published research on the non celiac gluten syndrome situation but it is
not well known in the gluten syndrome community.
The following section is devoted to that area of study and the researchers
and educators behind it. As the "fog lifts" on this phenomenon,
there is not perfect agreement, but it is exciting to watch this drama
unfold as our scientists, practitioners and patients work together to put
the pieces into the puzzle.
2007 update
Return to top
 Many more antibodies to test and the more tested the more patients test positive. Many more antibodies to test and the more tested the more patients test positive.
Several labs now offer tests
for additional antibodies (beyond gliadin and tTG). They also check more places in the immune system for these
antibodies. Current testing shows that many patients have one antibody but not
another depending on their situation. Therefore some researchers believe all the known antibodies should be
checked in all possible places.
Dr. Thomas O'Bryan
DC, CCN, DACBN
checked all the known
antibodies, including wheat, gliadin, gluten, gluteomorphins, and ttG, all
IgA, IgG, and IgM, in all his patients (350+ patients) over 3 years, and
achieved a 77% positivity rate for some gluten related antibody.
Research also indicates that
there are known
glutenins for which there are no tests at
this time.
The more antibodies
tested, the more patients test positive for immune response.
The more complete panels
of antibodies
include:
Gluten itself IgA, IgG,
IgM - the whole gluten molecule
Gliadin AGA IgA, IgG, IgM - a
piece of gluten
Gluteomorphins IgA, IgG, IgM
- a molecule that forms when gluten breaks down incorrectly.
Wheat - IgA, IgG, IgMthe
whole kernel - This ensures that anything not discovered in wheat is
tested.
tTG IgA, IgG, IgM- an enzyme
that elevates in some gluten syndrome reactions (the celiac villi process)
The additional places in the
immune system include:
IgA - Some celiac tests
check gliadin IgA, many don't.
IgG - Some celiac tests
check gliadin IgG, Many don't.
IgM - Very few labs check any
IgM antibodies.
At this time, these labs offer at least some of these additional tests in various
combinations.
ALCAT -
tests reactions of white
blood cells to gliadin, gluten, wheat, others. A controversial test..
Elisa/ACT Biotechnologies
- observes
lymphocyte reaction and checks gluten, gliadin, wheat, etc
Immunosciences Labs
- panels of ALL known antibodies, currently reorganizing
Optimum Health Resource
-
gliadin, wheat, gluten, and other substances, - IgG or IgA panels
Furthermore,
Enterolab
offers stool tests which do not test additional
antibodies, but this test returns much higher rates of positives than the
same tests in blood and claims a higher sensitivity.. This test is based on announced but unpublished research.
See
Lab Charts page for
current panels.
 Close: Many more antibodies
Close: Many more antibodies
 2008 Many more places for tissue damage beside, not necessarily including, villi.
2008 Many more places for tissue damage beside, not necessarily including, villi.
Dr. Vojdani, an immunologist
researcher from Los Angeles, California, has published research showing gluten
related damage to many tissues in the body, triggered by cellular
mimicry between the gluten related antibodies and innocent "look alike"
tissues all over the body. He finds the villi are just one of many
possible locations of target damage. Some patients have villi
damage, but in most patients the target damage is in some other organ or
tissue.
Full text here
 Close: Many more places for damage
Close: Many more places for damage
 2008 - Attention has finally turned to gluten and neurological issues.
2008 - Attention has finally turned to gluten and neurological issues.
Neurological tissue is
very very susceptible to gluten related damage according to more and more
researchers. Furthermore some say that if nerves are silenced by damage
there may be little warning until there is organ or function failure.
Check out these published quotes:
"The immune response
triggered by sensitivity to gluten may find expression in organs other
than the gut and the central and peripheral nervous systems are
particularly susceptible." -
M. Hadjivassiliou, 1997 see
reference below - Neuromuscular Disorder as a Presenting Feature of
Coeliac Disease
"Neurologic disorders or
findings were found in 51.4% of patients with Celiac Disease" -
Pediatrics Vol 113
No 6, June 2004 Nathanel Zelnik
"Two female patients
presented with cognitive decline that was attributed to Alzheimer's
dementia but ameliorated after the initition of gluten free diet.
The third patient had peripheral neuropathy that completely resolved after
initiation of the gluten free diet."
Celiac Disease Diagnosed in
the Elderly - J Clin Gastroenterol Vol 42,
No. 1, Jan. 2008 Yoav Lurie MD, Dan-Avi Landau, MD, Jorge Pfeffer MD,and
Ran Oran, MD Reprints: Yoav Lurie Gastroenterology Institute, Tel
Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Weizmann 6, Tel Aviv 64239, Israel
(email
dr-lurie@tasme.health.gov.il)
Copyright 2008 by Lippincott Williams & Williams
"Patients with
neurological disease of unknown etiology were found to have a much higher
prevalence of circulating antigliadin antibodies (57%) in their blood than
either healthy control subjects (12%) or those with neurological disorders
of known etiology (5%)."
M. Hadjivassiliou Gluten
Sensitivity as a Neurological Illness. See full reference below
"Mean age of ataxial onset
was 48 years old"
Gluten Ataxia in
Perspective - M. Hadjivassiliou, Brain (2003), 126, 685-691) See
full reference below
PubMed
research -
Gluten related neurological damage is now recognized as extensive by a
number of researchers. For an overview of published articles, go to
www.pubmed.gov
and type search term combinations such as "neurologic, or neurological, or
brain, or CNS, or MBP, or cerebellar" and "gluten, or celiac, or coeliac".
 Aristo Vojdani Neurology research and editorials Aristo Vojdani Neurology research and editorials
-
Immune response to dietary proteins, gliadin and
cerebellar peptides in children with autism.
Nutr Neurosci.
2004 Jun;7(3):151-61.Vojdani
A,
O'Bryan T,
Green JA,
Mccandless J,
Woeller KN,
Vojdani E,
Nourian AA,
Cooper EL. Section of Neuroimmunology, Immunosciences Lab., Inc., 8693
Wilshire Blvd., Ste. 200, Beverly Hills, California 90211, USA.
drari@msn.com
Full text here
Infections, toxic chemicals and dietary peptides
binding to lymphocyte receptors and tissue enzymes are major instigators
of autoimmunity in autism.
Int
J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2003
Sep-Dec;16(3):189-99
Vojdani A,
Pangborn JB,
Vojdani E,
Cooper EL
Lab. Comparative Immunology, Dept. Neurobiology,
UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
DrAri@msn.com
Full Text
here
-
In Celiac Disease, A Subset of Autoantibodies against Transglutaminase Binds
Toll-Like Receptor 4 and Induces Activation of Monocytes
Published Sept 19, 2006 Giovanna Zonomi1, Niccardo Navone2, Claudio
Lunardi2, Giuseppe Tidente1, Carerina Bason2,
Simona Sivori3, Buggero Beri2 Marzia Dolcino4,
Enrico Valletta5, Roberto Corrocher2, Antonio Puccetti3,4
1. Section of Immunology, Department of Pathology, University
of Verona, Italy
2. Section of Internal Medicine, Department of Clinical and Experimental
Medicine, University
of of Verona, Verona, Italy
3. Section of Histology, Departmant of Experimental Medicine, University of
Genova, Genova, Italy
4. Immunology Unit, Institute G. Gaslini, Genova, Italy,
5. Department of Pediatrics, University Hospital of Verona, Verona, Italy
Click for
abstract and full text
-
NEW!
The Immunology of
Immediate and Delayed Hypersensitivity to Gluten - European
Journal of Inflammation Vol 6 No. 1 1-10 (2008) Editorial - A. Vojdani
Beverly Hills, CA
(now Los Angeles, CA) T. O'Bryan, Warrenville, IL,( now Chicago, Il), G.
H. Kellermann Neuroscience, WI, USA
Full text here Note: This file
contains 2 articles from the journal.
Scroll to the top to find the Vojdani article.
-
NEW!
The Immunology of Gluten
Sensitivity Beyond the Intestinal Tract - Aristo Vojdani, PH.D, M.T.,
Thomas O'Bryan, D.C., C.C.N., DACBN,
Full text here
 Close: Aristo Vojdani
Close: Aristo Vojdani
 Mario Hadjivassiliou, Neurology, editorials here:
Mario Hadjivassiliou, Neurology, editorials here:
Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 2002;72:560-563
M
Hadjivassiliou, R A Grunewald and G A B Davies-Jones
Department of Neurology, The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Glossop road,
Sheffield, S10 2JF, UK
Correspondence to Dr. M Hadjivassiliou, Department of Neurology, The Royal
Hallamshire Hospital, Glossop Road, Sheffield, S10 2JF, UK
BMJ
1999; 318:1710-1
M
Hadjivassiliou, R. A. Grunewald, G A B Davies-Jones
Department of Neurology, The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Glossop road,
Sheffield, S10 2JF, UK
(m.hadjivassiliou@sheffield.ac.uk
M Hadjivassiliou, A K
Chattopadhyay, R. A. Grunewald, G A B Davies-Jones, A J Lobo
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1997;63:770-775 Department of
Neurology, The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Glossop road, Sheffield,
S10 2JF, UK
Department of Neurology, The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Glossop road,
Sheffield, S10 2JF, UK
(m.hadjivassiliou@sheffield.ac.uk)
 Close: Mario Hadjivassiliou
Close: Mario Hadjivassiliou
 Close: 2008 - Gluten and neurological issues.
Close: 2008 - Gluten and neurological issues.
2009
- GMO beet sugar
has
hit the market.
 Close: 2000's
Close: 2000's
 List of celiac specialists
in the US
in 2003
List of celiac specialists
in the US
in 2003
These few Celiac specialists worked hard to spread the word among their
peers and treat a deluge of newly informed patients. Several of them
identified celiac disease many years ahead of the 2003 research. These
experts are mainly focused on celiac villi damage. Some have moved beyond
to accept non celiac gluten syndrome. At this time most believe it
is not autoimmune, and still recommend the tTG screener and villi or skin
biopsy for dx of celiac disease.
They are all heroes and deserve our deep appreciation and respect.
 Alesio
Fassano MD - U of Maryland -
Contact here Alesio
Fassano MD - U of Maryland -
Contact here
Dr. Fasano's insistence that
indeed celiac disease is here in the United States and his persistance in
proving his case
paid off for thousands of Americans suffering the
consequences of undiagnosed gluten related ills. Dr. Fasano
originally moved from Naples, Italy to Baltimore, Maryland in the early
1990's to research children's diarrheal diseases. That research led
to discovery of zonulin, a tight junction regulator that influences
permeability of various mucosal and tissue barriers including the gut and
brain barriers. Building upon this discovery he is now involved in
development of a drug (AT
1001) that may be useful in various
autoimmune disorders such as celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis and
diabetes. Dr. Fasano recognizes that a
large number of the patients he sees react to gluten.
Celiac Disease update, Dec 2008, by Dr. Fasano.
 Dr.
Peter Green MD - U of Columbia -
Contact here Dr.
Peter Green MD - U of Columbia -
Contact here
Dr. Green is one of the few
specialists in the country who treated celiac disease before Dr. Fasano's
research project brought the disorder to public attention. He was
diagnosing patients in 1981, established and directed the Celiac Disease
Center at Columbia University in 2001. Dr. Green's book, "Celiac
Disease: a Hidden Epidemic 2006 is a "friendly" guide to the
many aspects of this disorder and is recommended reading. Dr. Green
acknowledges non celiac gluten sensitivity in his book and in practice.

Dr. Joseph Levy MD - Children's Digestive Health
Center - New York
Contact here
Dr Levy is Director of the
Children's Digestive Health Center at the Children's Hospital of New
York-Presbyterian in New York. He is a Professor of Clinical
Pediatrics at Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons.
He is on staff at the Celiac Disease Center at Columbia University.
 Dr.
Cynthia Rudert MD - Atlanta - Contact here Dr.
Cynthia Rudert MD - Atlanta - Contact here
Dr. Rudert is a
gastroenterologist in private practice in Altanta, Georgia. She graduated
University of Louisville, University of Louisville School of Medicine,
Louisville, KY in 1979 with postgraduate Gastroenterology training at
Emory University Hospital. Dr. Rudert is a
tireless supporter of the gluten
syndrome/celiac cause, and popular speaker at
conferences and support groups. She
maintains a sympathetic and supportive stance to her non celiac gluten
syndrome patients.
 Dr.
Guandalini MD - U of Chicago
Contact here Dr.
Guandalini MD - U of Chicago
Contact here
nnn
Dr. Guandalini, pediatrician, is a former
professor to Dr. Alesio Fasano in Italy, and founder and director of the
University of Chicago Celiac Disease Program. He is a rock solid
supporter of celiac disease and works diligently to gain the ear of his
American colleagues. He participated in the prevalence study published in
2003 and in establishment of international diagnostic criteria for celiac
disease. He is a respected expert specifically on villi damaged
celiac disease and helped hundreds of villi damaged patients. He has
published or contributed to over 100
articles.
 Dr.
Joe Murray MD - Iowa and then Mayo Clinic
Contact here Dr.
Joe Murray MD - Iowa and then Mayo Clinic
Contact here
Dr. Murray was born and schooled in
Ireland, and then moved to University of Iowa, and is now at Mayo Clinic.
He was one of the few specialists who diagnosed celiac disease in the US
in the late 1980's.
*"Dr. Murray of the Mayo
Clinic recalls that when he was a medical student in Galway, Ireland, in
the late 1970s and early 1980s, diagnoses of celiac disease were so common
they were "part of the medical wallpaper." After he moved to a job at the
University of Iowa in 1988, Dr. Murray once diagnosed a celiac alongside a
senior professor. "This will be the last such case you see, since we never
see this in America," Dr. Murray remembers the professor saying." Quote
from East Florida Celiac Group, Mike Martin
He published a
review on the
Widening Spectrum of Celiac Disease in
1999, and later
Dr. Murray expressed further surprise in 2006 at a
link found between celiac disease and neurological issues,
specifically dementia, observed in a Mayo study in 2006.
 Dr.
Michelle Pietzak MD - Los Angeles, CA
www.theglutenfreemd.com
Contact here Dr.
Michelle Pietzak MD - Los Angeles, CA
www.theglutenfreemd.com
Contact here
Dr. Pietzak,
pediatric
gasteroenterologist at Children's Hospital, Los Angeles, CA, and Director
of Center of Celiac Research West and medical advisor to the Celiac
Disease Foundation has produced 2 celiac based resources,
The Gluten Free MD 2006,
an audio educational CD, and
Understanding Celiac Disease and Gluten Intolerance,
an educational DVD, 2007, coproduced with
Dr. Alesio Fasano and Dr. Peter Green. To hear radio programs of Dr.
Pietzak's explanations of celiac disease and demos of the DVD visit her
informative website,
www.theglutenfreemd.com contains.
Dr. Pietzak differentiates celiac disease vs. non celiac gluten
intolerance as "autoimmune with possible accompanying nutritional and
other secondary effects", and "non autoimmune", respectively.
Biography
here
Radio talk here
 Dr.
John J. Zone MD - University of Utah, Dermatology
Contact here Dr.
John J. Zone MD - University of Utah, Dermatology
Contact here
Dr. Zone, schooled at University of Notre
Dame, NY, and Upstate Medical School, Syracuse, NY, has contributed
impressively to the celiac disease cause, and diagnosed and treated
patients for over 25 years. He also codeveloped a special
immunofluorescence staining process for blood and skin specimens.
This aided diagnosis and management of celiac disease.
Here are images of specimens so stained.
Dr. Zone's specialty in the celiac disease arena is dermatitis
herpetiformis. Dr. Zone became head of Dermatology at the University
of Utah in 1987and he is a staunch supporter and educator of the celiac
community. His
curriculum vitae is extensive.
 Close:
List of celiac specialists
Close:
List of celiac specialists
 List of Professionals who recognize non celiac gluten syndrome as
List of Professionals who recognize non celiac gluten syndrome as
often serious and often autoimmune.
Dr. Michael N. Marsh and
late Professor Anne Ferguson, UK
Dr. Michael N. Marsh, UK
- Retired author of
Celiac Disease: Methods and Protocols
printed in 2000 (see
sample pages on Amazon reader) . Dr.
Marsh is respected as a giant in the field of the Gluten Syndrome, called
"coeliac disease" when he practiced. In his day, all research was
focused on villi damage and he designed the Marsh Classification System
for
Villi Damage, which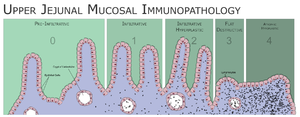 is in current use today (see
a recent challenge to this system). Dr. Marsh recently
publicly admonished his followers to respect the non celiac gluten
syndrome. His major work on stool testing, (originally this meant
washing out the contents of a patient's entire intestinal system) was
suspended unfinished and unvalidated when his research grant was
discontinued. He took retirement, his research partner Anne Ferguson
passed away, and the project came to a standstill. Later Dr. Ken
Fine, Baylor University, TX., see below, took up where Dr. Marsh and Anne
Ferguson left off, and developed a similar test. He developed a
method which required collection of just one bowel movement, a much more
practical procedure. Note: Dr. Marsh recently admonished his younger
peers at the XII International
Celiac Disease Symposium Conference held November 2006,
to take the non celiac
gluten syndrome seriously. His private response when shown a
complete list of available testable antibodies: "this is exactly
what we need." (That panel of antibodies returned a 77% positivity
rate in Dr. Thomas O'Bryan's entire practice over 3-4 years. Over
350 patients were tested.)
is in current use today (see
a recent challenge to this system). Dr. Marsh recently
publicly admonished his followers to respect the non celiac gluten
syndrome. His major work on stool testing, (originally this meant
washing out the contents of a patient's entire intestinal system) was
suspended unfinished and unvalidated when his research grant was
discontinued. He took retirement, his research partner Anne Ferguson
passed away, and the project came to a standstill. Later Dr. Ken
Fine, Baylor University, TX., see below, took up where Dr. Marsh and Anne
Ferguson left off, and developed a similar test. He developed a
method which required collection of just one bowel movement, a much more
practical procedure. Note: Dr. Marsh recently admonished his younger
peers at the XII International
Celiac Disease Symposium Conference held November 2006,
to take the non celiac
gluten syndrome seriously. His private response when shown a
complete list of available testable antibodies: "this is exactly
what we need." (That panel of antibodies returned a 77% positivity
rate in Dr. Thomas O'Bryan's entire practice over 3-4 years. Over
350 patients were tested.)
Professor Anne Ferguson, BSc, MB, ChB, PhD (Glas),
FRCPG, FRCP, FRCPE, FRCPath - Scotland
Anne
Ferguson (Anne Collee) a well loved and extremely accomplished
gastroenterologist, professor, researcher, and educator in a number of
medical fields shared Dr. Michael Marsh's final coeliac stool focused study. The
research project came to an unfinished and unvalidated halt when the
funding grant was withdrawn. Other researchers were unable to
duplicate their work. Professor Ferguson passed away after a short
illness in 1998 and Dr. Marsh retired. Their work was later continued by Dr.
Ken Fine, see below. Anne Ferguson's
biography and
obituary reveal Anne's remarkable and
compassionate legacy. A research article by Anne is
here

Dr. Mario Hadjivassiliou,
Sheffield England
Special thanks to
annelb of Gluten Free and Beyond Forums
for this comment and research list
Dr. Hadjivassiliou,
a neurologist in the UK, has been a leader in connecting central and
peripheral
neurological damage to gluten. He contends that gluten directly attacks
the nervous system. According to Dr. H, gluten sensitivity, without the
damage to the small intestine as seen in celiac disease, is all that is
needed for the nervous system to be damaged.
Contact here:
Dr. M Hadjivassiliou, Dept. of Neurology, The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Glossop Road, Sheffield, S10 2JF, UK
 Research by Dr. Mario Hadjivassiliou, neurologist - Sheffield, England
Research by Dr. Mario Hadjivassiliou, neurologist - Sheffield, England
mSpecial thanks to
annelb of Gluten Free and Beyond Forums
for the above comment and compilation of this research list
Correspondence: Dr. M Hadjivassiliou, Dept. of Neurology, The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Glossop Road, Sheffield, S10 2JF, UK
Click title for abstract
Autoantibodies in gluten ataxia recognize a novel
neuronal transglutaminase. Sept 2008
Cerebellar ataxia as a possible organ-specific autoimmune disease. Jul
2008
Gluten Ataxia. Jul 2008
A case of celiac disease mimicking amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Oct 2007
Adult Coeliac Disease Sept 2007
Gluten ataxia: passive transfer in a mouse model. Jun 2007
The Neurology of Gluten Sensitivity: Science vs
Conviction, April 2007
free full text
Myopathy associated with gluten sensitivity, Dec 2006
Dietary treatment of gluten neuropathy. Sept 2006
Neuropathy associated with gluten sensitivity, Nov 2006
Autoantibody targeting of brain and intestinal transglutaminase in gluten
ataxia. Feb 2006
Cerebellar abnormalities on proton MR
spectroscopy in gluten ataxia. July 2005 -
free full text
Are lower gastrointestinal investigations necessary in patients with
coeliac disease? Jun 2005
Multiple sclerosis and occult gluten sensitivity. Mar 2005
no abstract
Making the diagnosis of coeliac disease: is there a role for push
enteroscopy? Nov 2004
The immunology of gluten sensitivity: beyond the gut. Nov 2004
no abstract
Gluten sensitivity masquerading as systemic lupus erythematosus. Nov 2004
-
free full text
Choreic syndrome and coeliac disease: a hitherto unrecognised association,
Apr 2004
Dietary treatment of gluten
ataxia. Sept 2003 -
free full text
A primary care cross-sectional study of undiagnosed adult coeliac disease.
Apr 2003
Gluten ataxia in perspective: epidemiology, genetic susceptibility and
clinical characteristics. Mar 2003 -
free full text
Gluten Sensitivity: Time to move from Gut to Brain. Jan/Feb 2003 -
free full text
The humoral response in the pathogenesis of gluten ataxia. Apr 2002
no abstract
Gluten sensitivity as a
neurological illness May 2002 -
free full text.
Headache and CNS white matter abnormalities associated with gluten
sensitivity. Feb 2001
Gluten sensitivity: a many headed hydra. Jun 1999 -
free full text
Clinical, radiological, neurophysiological, and neuropathological
characteristics of gluten ataxia. Nov 1998
Neuromuscular disorder as a presenting feature of coeliac disease. Dec
1997 -
free full text
Does cryptic gluten sensitivity play a part in neurological illness? Feb
1996
 Close:
Dr. Mario Hadjivassiliou
Close:
Dr. Mario Hadjivassiliou
 mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm
Return to top
mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm
Return to top
Dr. James Braly, MD. and
Dr. Ron Hoggan ED.D
Contact Dr Braly
Dr. Braly MD and Dr. Ron
Hoggan Ed.D collaborated in 2002 on their courageous book, "Dangerous
Grains" which clearly and convincingly discussed non celiac
gluten reactivity at a time
when it was not acknowledged by celiac "villi focused" authorities. Dr.
Braly, MD, is an experienced and personally gluten sensitive allergist.

Ron Hoggan Ed.D.
Contact
Ron Hoggan
Ron Hoggan Ed.D. holds a PhD in education and is a high school teacher. He
is dx celiac and has written an impressive number of articles on the
gluten syndrome. Check out the
Dangerous Grains website. A long list of
Ron's articles is here. Ron fought an uphill battle to encourage many
confused patients and parents to respect non celiac gluten syndrome and
finally is receiving the respect he richly deserves. Ron recently wrote
"Get
the Iron Edge", which highlights the particular
challenges of gluten syndrome patients to maintain iron levels. His
insightful and very worthwhile DVD "Smarten up" is a compilation of 3
talks on the effect of the gluten syndrome for children and students from
his qualified and compassionate perspective as a personally celiac
affected educator.
"Smarten Up" is an invaluable and highly
recommended resource for parents, grandparents and teachers. (This
website has no financial interest in products or services mentioned here.)

Dr. Kenneth Fine, MD Gastroenterologist
Contact Dr. Fine
Dr. Fine, MD, is a respected
gastroenterologist from Dallas, TX. Formerly associated with Baylor
University, he is involved in announced but unpublished stool testing
research and owns an independent lab for internet based, home collection
gluten sensitivity stool tests.
Dr. Fine took up the research left unfinished by Dr. Michael N Marsh and
Anne Ferguson (UK), originally in the study of microscopic colitis. He
drew a connection between microscopic colitis and the gluten syndrome and
eventually left Baylor and set up an independent accredited lab around
2000 to offer his stool test and a few other related tests directly to the
public.
Dr. Fine is criticized for the high number of positives processed in his
lab compared to celiac "villi focused" labs. However many patients find
that his test matches their own experience. His results match findings by
Dr. Thomas O'Bryan's practice and Dr. Vojdani's lab results. Dr. Fine also
recognizes more genes than celiac focused specialists. Several very
informative essays explaining his perspective are posted on his website
www.enterolab.com .
 Dr.
Fine's alternative perspectives of the gluten syndrome vs. standard celiac
concepts Dr.
Fine's alternative perspectives of the gluten syndrome vs. standard celiac
concepts
Dr. Fine proposes the
following modifications to dx criteria for recommendation of the gluten
free diet.
-
Stool provides earlier
markers of gluten reactivity.
-
His intestinal FUNCTION test
ie, how well does the gut work?, based on fat absorption, is advised.
-
Genes HLA DQ 1, 2, 3, 8
are gluten genes, each expressed more or less in various tissue injury.
-
Gluten syndrome is often beyond the
gut, ie. villi are not always damaged early on so biopsy is a imperfect
gold standard. Elevated antibodies indicate a sensitized immune
system, go gluten free.
-
If undigested gluten ends up in the
wrong place, ie, it slips past the gut (leaky gut) or another mucosal
barrier, if a gluten related gene is present, the immune system will
react.
Patients are confused by
conflicting opinions of Dr. Fine's ideas and his test. In the
absence of published peer reviewed data at this time they wonder who he is
and why he has not published his work.
Dr. Fine is well qualified as
a gastroenterologist, a fact acknowledged even by is critics. Upon
inquiry among those who have known him in his local medical arena and
knowledgeable folks in the gluten syndrome field I learned that he appears
to have 3 interests; his gastroenterology research, his music, and helping
people. He prefers to invest in research than easy living., He loves
to play his guitar and sing under the stars in the desert with kids and
their families to society life, and is also an accomplished musician.
He has struggled with his own gastrointestinal issues for years and is on
the gluten free diet.
Dr. Fine has published other
research articles in the past. He announced his research 3 years ago
in 2006 shortly after a patent was obtained for the test. It is the
opinion of some that Dr. Fine has further delayed publishing his work for
specific study related reasons.
This work is not peer
reviewed, duplicated or validated. Only one parallel study has been
performed which claims not to find stool tests of value. Drl. Fine
takes issue with the methods used in that study. Other professionals claim
to have tried to duplicate Dr. Fine's test without success. However,
over the past 5 years, public and in many cases professional confidence
has risen very significantly as more and more patient's experiences match
his test results.
(This
website has no financial interest in products or services mentioned here.)
Return to top
 Close: Dr. Kenneth Fine
Close: Dr. Kenneth Fine

Dr. Aristo Vojdani, PhD,
Immunology, MT
Contact
here
Dr. Aristo Vojdani is a
respected immunologist/researcher from Los Angeles, formerly Beverly Hills.
He is well known in the biomedical autism circuit.
He owns
Immunosciences Laboratories, a specialty lab currently under
reorganization. They plan to reopen Spring of 2009 to concentrate on
very detailed and progressive gastrointestinal and autoimmune testing
panels. Dr. Vojdani has published numerous times on the effects of
toxins, gluten and other cross reactive foods and substances on the brain
and neurological system and many other body tissues. His lab plans to
offer detailed and progressive test panels for the gluten syndrome
starting spring, 2009. The test goals include all possible known
antibodies for which tests are available and a progressive system of
testing until a positive is obtained, which controls cost for the patient.
Be sure to visit his website when it is reposted to check out his array of
excellent articles.
 Dr. Aristo Vojdani, Ph.D,
MT proposes the following serious alterations to current concepts of
gluten testing
and gluten's effects on many body systems. Dr. Aristo Vojdani, Ph.D,
MT proposes the following serious alterations to current concepts of
gluten testing
and gluten's effects on many body systems.
-
There are many more
antibodies to check beside gliadin and tTG. Others
include gluteomorphins, gluten itself, wheat and AGA-tTG. Check IgA,
IgG, and IgM for each antibody.
-
tTG is not always elevated in many
gluten related reactions so tTG as a general screener is inappropriate.
-
Molecular, or cellular
mimicry of antibodies with innocent tissue - Gluten related antibodies can
cross react or bind with "look alike" parts of innocent tissues all over
the body. This instigates damage by "friendly fire" since the
antibodies attract killer cells to that tissue. Villi are not
necessarily injured in these cases. This is called molecular or
cellular mimicry.
-
Villi damage is only
one particular type of reaction out of many other possible serious
autoimmune reactions. The celiac reaction not only damages villi but
can damage many other tissues also. See
Medical Diagrams
-
Villi biopsy is in
inappropriate diagnostic gold standard for gluten free diet since villi are only damaged
in certain (relatively rare, 1 in 100) reactions. Some
folks do have celiac villi damage. Most do NOT but may be severely damaged in
other tissues. Invasive and expensive villi biopsy should be
reserved for other reasons to examine the gut. Antibodies or diet
response are diagnostic in and of themselves.
-
The brain and nervous
system is very susceptible to gluten related damage by molecular mimicry
between antibodies and cerebellar tissue, Neurofilaments and myelin basic
protein (nerve insulation.
-
Processed wheat combined
with chemicals can create allergic response in persons who normally do not react to wheat.
-
TOXINS are the "Big Guns"
behind the gluten syndrome. For instance, organophosphates and heavy
metals are fingered in inhibition of DPP IV, an important digestive enzyme
that digests milk and gluten and also plays an important role in the
immune system. Chemical injury, ie. toxins, injure the tight
junctions between gut cells to create leaky gut through which gluten
peptides slip into the lymph and blood systems and are recognized as
enemies by the immune system. Stress and infections also trigger
leaky gut. (See Medical Diagrams with references.)
-
Genes are NOT NEEDED to
instigate a gluten related adverse reaction. Toxins are enough to
create an adverse cascade of reactions. Genes predispose.
 Close: Dr. Aristo Vojdani, Ph.D, MT
Close: Dr. Aristo Vojdani, Ph.D, MT
 Aristo Vojdani PhD, Thomas O'Bryan - Immunology research:
Aristo Vojdani PhD, Thomas O'Bryan - Immunology research:
-
Immune response to dietary proteins, gliadin and
cerebellar peptides in children with autism.
Nutr Neurosci.
2004 Jun;7(3):151-61.Vojdani
A,
O'Bryan T,
Green JA,
Mccandless J,
Woeller KN,
Vojdani E,
Nourian AA,
Cooper EL.
Section of Neuroimmunology, Immunosciences Lab., Inc., 8693
Wilshire Blvd., Ste. 200, Beverly Hills, California 90211, USA.
drari@msn.com
Full text here
Infections, toxic chemicals and dietary peptides
binding to lymphocyte receptors and tissue enzymes are major instigators
of autoimmunity in autism.
Int
J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2003
Sep-Dec;16(3):189-99
Vojdani A,
Pangborn JB,
Vojdani E,
Cooper EL
Lab. Comparative Immunology, Dept. Neurobiology,
UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
DrAri@msn.com
Full Text
here
-
In Celiac Disease, A Subset of Autoantibodies against Transglutaminase Binds
Toll-Like Receptor 4 and Induces Activation of Monocytes
Published Sept 19, 2006 Giovanna Zonomi1, Niccardo Navone2, Claudio
Lunardi2, Giuseppe Tidente1, Carerina Bason2,
Simona Sivori3, Buggero Beri2 Marzia Dolcino4,
Enrico Valletta5, Roberto Corrocher2, Antonio Puccetti3,4
1. Section of Immunology, Department of Pathology, University
of Verona, Italy
2. Section of Internal Medicine, Department of Clinical and Experimental
Medicine, University of Verona, Verona, Italy
3. Section of Histology, Departmant of Experimental Medicine, University of
Genova, Genova, Italy
4. Immunology Unit, Institute G. Gaslini, Genova, Italy,
5. Department of Pediatrics, University Hospital of Verona, Verona, Italy
Click for
abstract and full text
-
NEW!
The Immunology of
Immediate and Delayed Hypersensitivity to Gluten - European
Journal of Inflammation Vol 6 No. 1 1-10 (2008) Editorial - A. Vojdani
Beverly Hills, CA
(now Los Angeles, CA) T. O'Bryan, Warrenville, IL,( now Chicago, Il), G.
H. Kellermann Neuroscience, WI, USA
Full text here Note: This file
contains 2 articles from the journal.
Scroll to the top to find the Vojdani article.
-
NEW!
The Immunology of Gluten
Sensitivity Beyond the Intestinal Tract - Aristo Vojdani, PH.D, M.T.,
Thomas O'Bryan, D.C., C.C.N., DACBN,
Full text here
-
NEW!
The Gluten
Response in Children with Celiac Disease is Directed toward Multiple
Gliadin and Glutenin Peptides - Gastroenterology 2002; 122:1729-1737 Willemijen Vader, Yvonne Kooy, Peter
Van Veelen, Arnoud de Ru, Diana Harris, Willemien Benckhuijsen, Salvador Pena, Luisa
Mearin, Jan Wouter Drijfhout, and Frits Koning Departments of
Immunohematology and
Blood Transfusion and Paediatrics, Leiden University Medical Centre,
Leiden, The Netherlands; and the Free University, Amsterdam, The
Netherlands
Full text here
 Close: Aristo Vojdani, PhD
Close: Aristo Vojdani, PhD
Return to top

Dr. Thomas O'Bryan
Contact here
Dr. O'Bryan
is a functional medicine practitioner in Chicago area. His excellent
research reviews on various aspects of the gluten syndrome are incredibly
clear and well presented. Dr. O'Bryan works with Dr. Aristo Vojdani in
research and test development. He has produced detailed testing protocols
that produce impressive rates of positivity that match most patient's
experience. (The secret? He tests as many gluten related antibodies as
possible! Over 4 years he ran a detailed panel of gluten related
antibodies (12-15 tests) on all patients in his practice with a 77%
positivity rate. Many of those patients tested positive for antibodies
other than gliadin and tTG and IgA, IgG, and IgMs were all checked for
each antibody. He also ran cross reactive foods and a panel of antibodies
to tissues known to be particularly susceptible to gluten damage. Dr.
O'Bryan completed an outstanding and highly appreciated speaking circuit in
the USA in 2008 in which he addressed 3000 medical doctors and
practitioners on the wider scope of the gluten syndrome. His planned 2009
circuit focuses on food allergies in general. Often he speaks to patient
support groups the evening before the main presentation to professionals.
If he comes to your area BE SURE to arrange a special event for your group
to hear these incredibly well presented and informative lectures. Watch
for a post of his schedule soon.
Dr. O'Bryan's first research review
"Unlocking the Mystery of Wheat and Gluten
Intolerance"
is available in DVD format
here and
here and
here.
His second research review for patients (3 hours) is due to be posted free
on this website soon.
Click here for his 90 minute audio talk,
"I'm gluten free but I don't feel great"
also on the home page of this website. All these talks are excellent
resources on the gluten syndrome.
(This website has no
financial interest in products or services mentioned here.)

Dr. Rodney Ford, MD, MB
FRACP, ASM Professor, "Dr. Gluten" New Zealand
Contact here
Dr. Ford is an experienced
pediatrician with a specialty in food allergies and particularly the
gluten syndrome. Dr. Ford coined the term, "The Gluten Syndrome".
Dr. Rodney Ford proposes that if the nerves in an organ or system are
damaged in some cases there may be little discomfort or few symptoms until
there is serious dysfunction or organ failure. The very nerves that give
warning are themselves damaged/silenced. But slowly dysfunctional nerves
in an organ, for instance, affect the health and function of that organ or
system. This phenomenon of silenced nerves may be partly why many folks
who still think they are fine discover they have the gluten syndrome only
after a relative is diagnosed. Dr. Ford believes nerves are very
very susceptible to gluten related damage.
Dr. Ford cites a case in his practice of an encopretic school aged child
(the child experienced soiling accidents long past potty training age).
After the gluten free diet was introduced, this distressing problem
resolved. The nerves in that section of the digestive tract healed and the
child knew when it was time to visit the toilet.
www.drgluten.com
Dr. Ford has written a number of
books on the gluten syndrome and his website
and video clips are very helpful.
Dr Ford also participated in the New Zealand Cot Death Study. Dr. Ford was
part of a team that traveled the world persuading professionals to teach
parents to position infants on their backs when sleeping. This project
reduced the tragedy of crib death (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, SIDS) to
a mere fraction of previous mortality rates.
Coming:
Dr. Scott Lewey - Colorado
Dr.Shari Lieberman - Author
The Gluten Connection
Dr. Steve Wangen - Author
Healthier Without Wheat
Drs. Richard and Vikki
Peterson - Authors The Gluten Effect
 Close:
List of Professionals
Close:
List of Professionals
Return to top
|



 Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur

 in the 1930's to observe these peoples, their diets, food preparation methods, and their overall health.
He lined up villages to count cavities, made notes on general health, and
took food and saliva samples back to his laboratory. He
found 11 consistent dietary and cultural similarities between these
very diverse isolated peoples around the world. He also
found overall better health in the traditional cultures, and fine, straight teeth set in wide faces,
with dental arches that had plenty of room for wisdom teeth, and very low
incidences of cavities. He also observed a heartbreaking decline in
overall health, susceptibility to illness, and “dental deformities”,
meaning narrowed dental arches and crowded crooked teeth, other physical degradations, and many
degenerative health conditions wherever these peoples came in contact with
civilization and adopted modern foods. Other researchers of his era who performed
similar studies had parallel findings.
in the 1930's to observe these peoples, their diets, food preparation methods, and their overall health.
He lined up villages to count cavities, made notes on general health, and
took food and saliva samples back to his laboratory. He
found 11 consistent dietary and cultural similarities between these
very diverse isolated peoples around the world. He also
found overall better health in the traditional cultures, and fine, straight teeth set in wide faces,
with dental arches that had plenty of room for wisdom teeth, and very low
incidences of cavities. He also observed a heartbreaking decline in
overall health, susceptibility to illness, and “dental deformities”,
meaning narrowed dental arches and crowded crooked teeth, other physical degradations, and many
degenerative health conditions wherever these peoples came in contact with
civilization and adopted modern foods. Other researchers of his era who performed
similar studies had parallel findings.


 were again available.
were again available.  Food
Pyramid with grains on the bo
Food
Pyramid with grains on the bo





 Dr.
Guandalini MD - U of Chicago
Dr.
Guandalini MD - U of Chicago
 Dr.
Michelle Pietzak MD - Los Angeles, CA
Dr.
Michelle Pietzak MD - Los Angeles, CA Dr.
John J. Zone MD - University of Utah, Dermatology
Dr.
John J. Zone MD - University of Utah, Dermatology is in current use today (
is in current use today (




